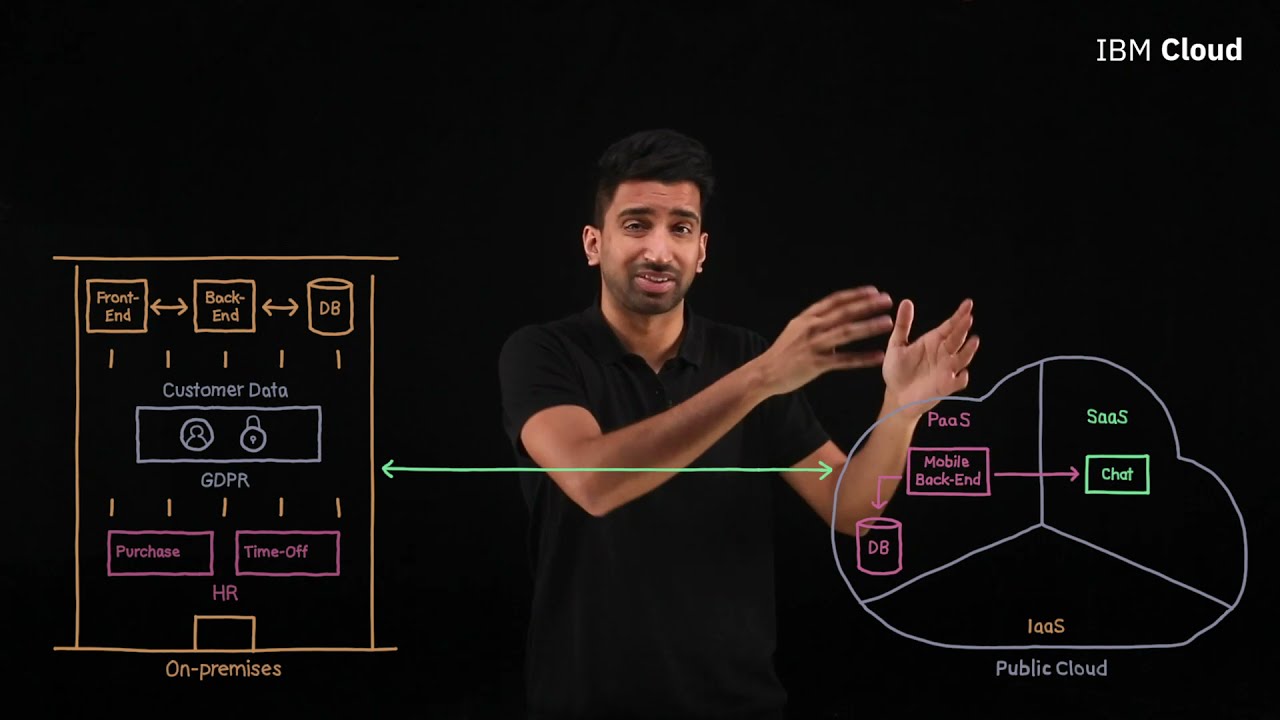
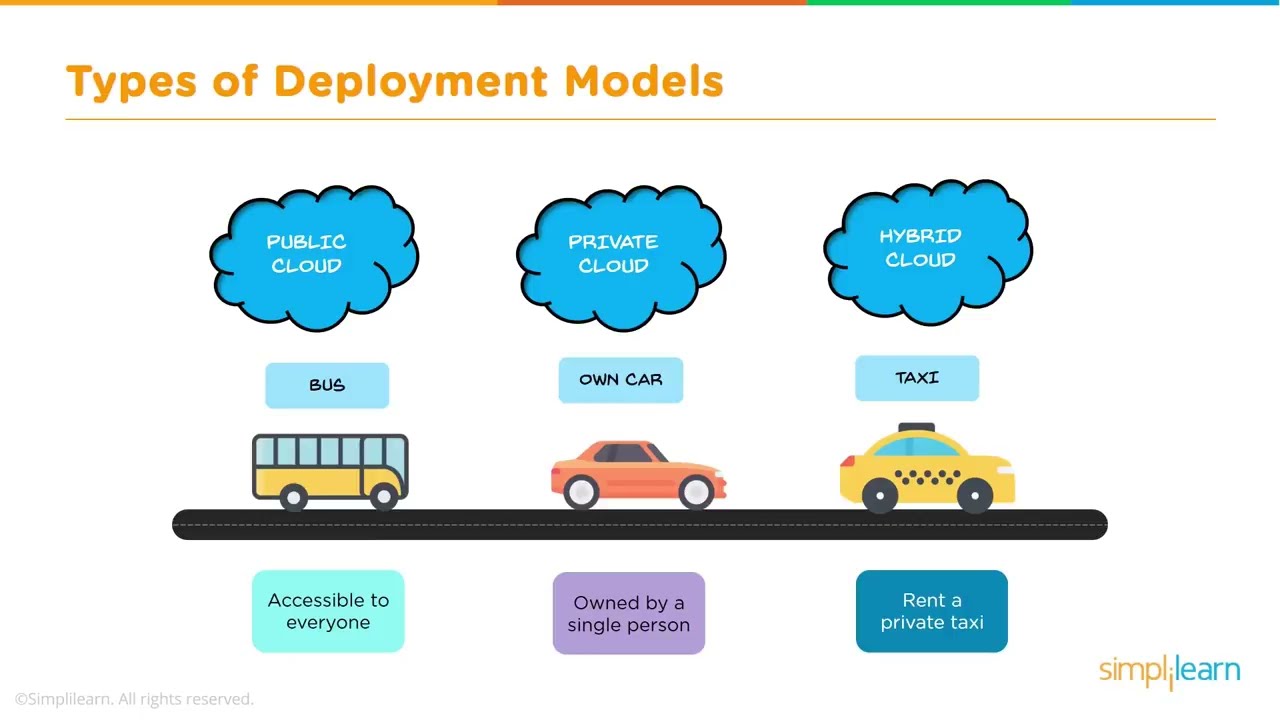
As businesses continue to expand and move towards digital transformation, they often find themselves facing challenges in managing data across various locations and environments. This is where hybrid cloud infrastructure comes into play. It offers the best of both worlds by combining public and private clouds into a unified solution that provides flexibility, security, and scalability. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at hybrid cloud infrastructure, its benefits, how to use it, comparisons with other cloud models, and provide advice on its implementation.
What is Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure?
Hybrid cloud infrastructure combines the features of both public and private clouds to create a single, integrated cloud solution. Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party service providers, while private clouds are owned and managed by an organization’s IT team. Combining these two models allows organizations to leverage the strengths of each to create a more efficient and flexible cloud environment.
Hybrid cloud infrastructure allows for the seamless transfer of workloads between public and private clouds, enabling organizations to choose the most suitable location for each workload. For instance, sensitive data can be stored within the secure confines of a private cloud, while non-sensitive data can be stored in a public cloud for easier accessibility.
IBM has been pushing laborious on being a aggressive menace in enterprise cloud, however is much behind the leaders like Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud. It’s newest technique to turn out to be extra related, along with shopping for RedHat for its cloud experience, is to develop a sequence of “straightforward on-ramp” Cloud Paks that it claims can considerably scale back the period of time needed for enterprises to be cloud-enabled. However is that this sufficient to alter the potential of IBM to compete in a extremely aggressive fashionable cloud surroundings?
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
- Flexibility: With hybrid cloud infrastructure, organizations have greater flexibility when it comes to workload management. They can choose where to store their data and applications based on specific business requirements.
- Scalability: Hybrid cloud infrastructure supports rapid scaling, which means organizations can easily add or remove resources as required. This helps control costs and avoids wasting resources.
- Cost Savings: By leveraging both public and private clouds, organizations can save on capital expenditures (capex) and operational expenditures (opex). They can use public clouds for less-sensitive workloads and only invest in expensive private clouds where necessary.
- Security: Hybrid cloud infrastructure provides enhanced security measures for sensitive data, which is hosted on private clouds. This improves regulatory compliance and helps avoid data breaches.
How to Use Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
Before implementing hybrid cloud infrastructure, organizations must assess their needs and consider the following steps:
With certifications accessible from distributors like Microsoft, NetApp, and Crimson Hat, in addition to third events such because the Cloud Certificates Council and International Data, IT professionals have loads of alternatives to pursue focused coaching within the hybrid cloud.
Lynne Williams, professor on the College of Enterprise and Data Expertise at Purdue College International, which incorporates instruction on hybrid cloud in its cyber safety and IT grasp's diploma applications, says coaching and certification are important for bigger organizations and those who fall beneath regulatory oversight.
- Determine which workloads are better suited for public or private clouds.
- Evaluate the available cloud providers and select the ones that meet your requirements.
- Develop a cloud migration strategy that includes timelines and contingencies.
- Implement the necessary infrastructure changes and test the system before going live.
Examples of Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
Hybrid cloud infrastructure is applicable in various industries. Here are some examples:
- Healthcare: Hospitals can use hybrid cloud infrastructure to store patient information securely within a private cloud while leveraging public clouds for non-sensitive workloads such as email and collaboration tools.
- E-commerce: Online retailers can use hybrid cloud infrastructure to manage their online storefronts, with sensitive customer information stored within a private cloud and non-sensitive data hosted on public clouds.
- Finance: Banks and financial institutions can use hybrid cloud infrastructure to securely store customer data while leveraging public clouds for non-sensitive applications such as emails and file-sharing.
Comparing Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure with Other Models
- Public Cloud: Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party service providers and offer affordable pay-as-you-go pricing models. However, deploying critical workloads on public clouds may not be suitable due to potential security and performance issues.
- Private Cloud: Private clouds provide enhanced security measures and greater control over data, but they require significant upfront capital expenditures and ongoing operational costs.
- Multi-Cloud: Multi-cloud involves using multiple cloud providers to host different workloads. While it provides flexibility, it can also lead to increased complexity and management challenges.
Compared to these other models, hybrid cloud infrastructure offers the best of both worlds, allowing organizations to leverage the strengths of public and private clouds while mitigating their weaknesses.
To be absolutely dedicated to safety means being keen to decide to the exhausting work. "What I've historically heard from most individuals is, 'We need to do it and never be disruptive'," Younger says. "These two issues simply do not go hand in hand as you implement tight safety. We have had the posh of getting executives...who imagine in safety first."
Hyperconvergence—combining storage, computing, and networking on a single {hardware} system—additionally performs an essential function in Ceridian's long-term technique. "Now we have a footprint in hyperconvergence with what we name our bureau panorama," Younger says. Hyperconvergence know-how guarantees to assist Ceridian unify its non-public, public, and distributed clouds, permitting the corporate to scale operations, simplify deployments, improve reliability, and decrease prices, amongst different advantages.
Advice for Implementing Hybrid Cloud Infrastructure
- Plan Ahead: Before implementing hybrid cloud infrastructure, it’s important to plan and evaluate your business requirements, potential challenges, and available resources.
- Start Small: It’s best to start with small workloads before scaling up to larger ones. This helps minimize risks and allows organizations to test their systems thoroughly.
- Choose the Right Provider: When selecting a cloud provider, consider their track record, security measures, and compliance certifications.
- Stay Compliant: Ensure that hybrid cloud infrastructure complies with all regulatory requirements, especially if sensitive information is involved.
- Train Your Staff: Provide adequate training for staff on how to use and manage hybrid cloud infrastructure. This will ensure that they understand how to leverage its benefits and avoid costly mistakes.
FAQs
Q1. What are the key benefits of hybrid cloud infrastructure?
A1. Hybrid cloud infrastructure offers greater flexibility, scalability, cost-savings, and security.
Q2. Is hybrid cloud infrastructure suitable for all industries?
A2. Yes, hybrid cloud infrastructure can be used across various sectors, including healthcare, e-commerce, finance, and more.
Q3. How can I determine which workloads are better suited for public or private clouds?
A3. Consider the sensitivity of the data, performance requirements, and regulatory compliance when deciding which cloud model to use.
Q4. Is hybrid cloud infrastructure more expensive than other cloud models?
A4. While there may be additional costs associated with managing multiple cloud environments, hybrid cloud infrastructure can ultimately save organizations money by leveraging cost-effective public clouds for non-sensitive workloads.
Q5. What are some common challenges when implementing hybrid cloud infrastructure?
A5. Challenges may include ensuring data security and compliance, managing multiple cloud providers, and integrating legacy systems with new cloud infrastructure.
Conclusion
Hybrid cloud infrastructure provides a flexible and scalable solution for managing workloads across multiple cloud environments. By leveraging its benefits, organizations can reduce costs, enhance security measures, and improve their overall cloud management capabilities. Implementing hybrid cloud infrastructure requires careful planning, evaluation of business requirements, and selecting the right provider. However, the potential benefits make it a worthwhile investment for many organizations.