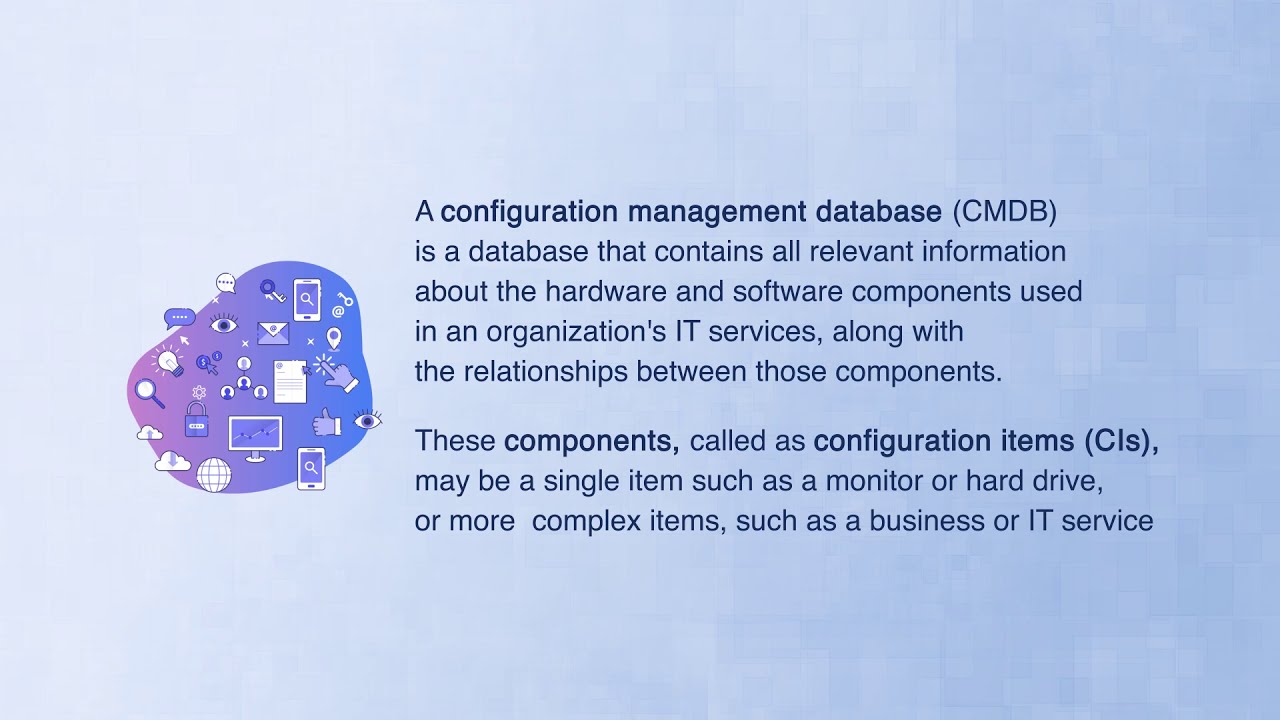
As businesses grow, the management of data and assets becomes more complex. To keep up with this growth, organizations need a reliable system that can help them manage their configurations and ensure that all their assets are functioning as expected. This is where a configuration management database (CMDB) comes into play.
A CMDB is a repository that stores all information related to an organization’s IT infrastructure. It helps organizations to maintain a complete inventory of their assets and their configurations, including hardware, software, and network components. This article will explore the importance of a configuration management database in streamlining business operations and provide advice on how to use it effectively.

A CMDB is a centralized database that contains information about all the IT assets and configurations within an organization. It acts as a single source of truth for the entire IT infrastructure, acting as a reference point for configuration items, change requests, and incidents.
Most organizations are at the least experimenting with cloud workloads, however many even have a really combined cloud surroundings. Of the organizations working cloud workloads, we estimate at the least 80 % have a multi-cloud surroundings that features entry to each on-prem and public cloud cases, in addition to utilizing a number of suppliers (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google, Oracle, IBM, SAP, and many others.). This makes the world of cloud deployments very complicated.
The purpose of a CMDB is to enable organizations to track and manage their IT assets better. It provides a framework for modeling and managing relationships between IT assets, which helps organizations understand the impact of changes made to one asset on others.
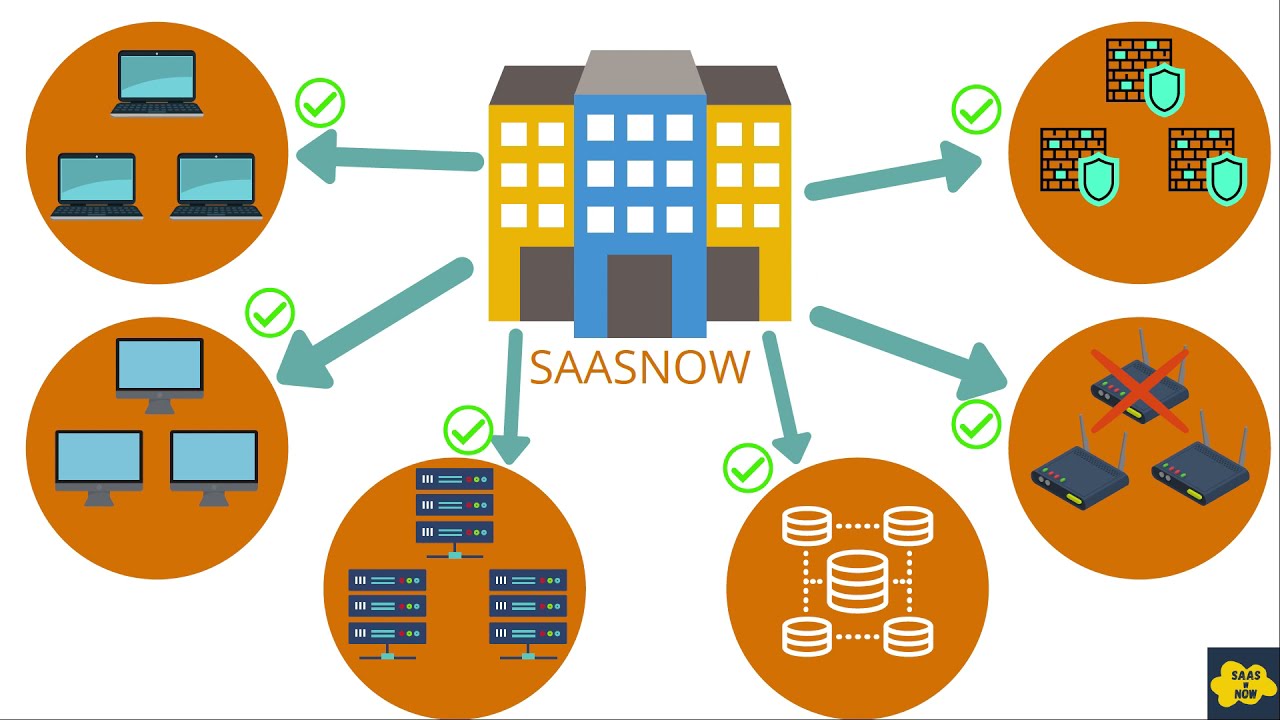
A CMDB begins by identifying all the configuration items (CIs) within an organization. These CIs can include hardware, software, applications, network devices, and even people. Once the CIs are identified, they are added to the CMDB, along with their attributes and relationships.
When an organization wants to make changes to its IT infrastructure, it can use the CMDB to understand the potential impact of those changes on other CIs. For instance, if an organization wants to upgrade its servers, it can use the CMDB to identify all the applications that run on those servers and understand how the upgrade might impact those applications.
One real-world example of a CMDB in action is NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). JPL uses a CMDB to manage its IT infrastructure, including the Mars Rover. The CMDB helps JPL track the various components that make up the rover and provide a complete picture of its current state.
Another example is the banking industry. Banks use CMDBs to manage their IT infrastructure, which includes ATMs, point-of-sale systems, and mobile banking applications. A CMDB helps banks keep track of all these devices, understand how they are interconnected, and ensure that they are functioning optimally.
There are several advantages to using a CMDB in an organization. These include:
A CMDB provides a complete picture of an organization’s IT infrastructure, including all the CIs and their relationships. This visibility helps organizations make informed decisions about their IT assets and improve their overall management.
When issues arise within an IT infrastructure, a CMDB can help organizations quickly identify the root cause of the problem. By understanding the relationships between CIs, organizations can isolate the CI causing the issue and resolve it faster.
A CMDB helps organizations understand the impact of changes made to their IT infrastructure before those changes are implemented. This reduces the risk of unintended consequences and helps organizations avoid costly downtime.
To use a CMDB effectively, organizations need to follow a few best practices:
Before implementing a CMDB, organizations should define clear objectives for what they want to achieve with the database. This will help them focus on the data and relationships that are most important.
To get the most out of a CMDB, it is essential to maintain accurate data. Organizations should regularly review the data in the CMDB to ensure that it is up-to-date and complete.
To ensure that staff can use the CMDB effectively, organizations should provide training on how to use the database. This will help staff understand the importance of accurate data and how to use the CMDB to its full potential.
While there are several IT asset management tools available, a CMDB offers some unique advantages:
A CMDB provides a centralized repository for all information related to an organization’s IT infrastructure. This holistic view helps organizations manage their IT assets more effectively and make informed decisions about their IT investments.
A CMDB helps organizations understand the impact of changes made to their IT infrastructure before those changes are implemented. This helps organizations avoid costly downtime and reduce the risk of unintended consequences.
In summary, a configuration management database is a crucial tool for managing an organization’s IT infrastructure. By providing a centralized repository for all configuration items, a CM DB helps organizations improve their visibility into the IT infrastructure, reduce risk, and resolve issues faster. To use a CMDB effectively, organizations should define clear objectives, maintain accurate data, and provide training for staff to use the database properly.
While there are several IT asset management tools available, a CMDB offers unique advantages. It provides a holistic view of an organization’s IT infrastructure and enables better change management.
In conclusion, a configuration management database is an essential tool for streamlining business operations. By using a CMDB effectively, organizations can manage their IT assets more effectively, avoid costly downtime, and make informed decisions about their IT investments. Investing in a CMDB can help organizations stay ahead of the curve and ensure that their IT infrastructure supports their business goals and objectives.