Do you know that you could ask your Linux system to let you know what upgrades can be found for the packages put in on it? You is likely to be stunned by what number of you’ll see, particularly when you’re utilizing the present launch and don’t have your system arrange for frequent or automated updates.
Updates play an vital function in retaining your Linux techniques safe and performing properly. Since most packages are up to date as fixes or enhancements to the code change into accessible, it’s onerous to foretell what number of will present up on any specific day. (Word: Updates ought to be executed when your system just isn’t performing different vital duties.)
To examine what updates are at the moment accessible on your Fedora or associated system, use a command like this:
These 5 particular use instances will finally be expanded by IBM and also will be made out there to the ecosystem for enlargement by particular person corporations and/or distributors. And though these Cloud Paks are optimized to run on the IBM Cloud, as a result of they're constructed on prime of OpenShift they can run on just about any cloud basis, making a no-lock-in answer that must be extra palatable to corporations who aren't IBM-centric or unique.
On a system which hasn’t been upgraded in every week or so, you may simply see numbers like these proven under the place we rely all updates after which these which are safety updates.
To use the accessible upgrades, you merely use a command like that proven under. The —refresh possibility marks the metadata as expired and forces the system to revalidate the cache.
Discover how the replace course of goes by means of quite a lot of phases—upgrading, cleanup and verifying—and ends with an inventory of the up to date packages.
At this level, no extra upgrades can be found. For those who like, you possibly can confirm this by repeating the “listing upgrades” command above. You need to see a line like this with no updates listed.
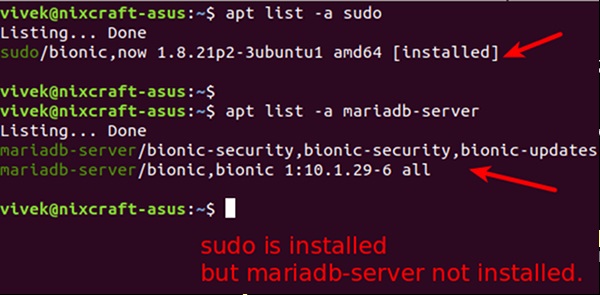
To see what updates can be found on Ubuntu, Mint, and associated techniques, the command to make use of is apt listing –upgradable. It’ll present an inventory of up to date packages.
Word that whenever you run the command sudo apt replace, the ultimate line of output suggests this command:
The sudo apt improve -y command can then be used to use all the accessible updates to put in packages. As soon as that course of is full, you possibly can repeat the apt listing –upgradable command to point out that there aren’t any extra accessible updates.
Some Linux admins and customers replace their techniques each day or weekly. Others set their techniques up for automated updates. In any case, it’s good to maintain your system up to date pretty usually and to have some simple instructions available to confirm that your system is up-to-date.